Planning is an intrinsic element of project management that comes at the beginning of the process, just after the project launch. Once this has been validated, it then makes way for project planning.. Generally speaking, good planning defines the stages of a project. It allows clear identification of objectives, definition and organisation of tasks and resources, and above all methodical working to meet the budget and deadlines. Its aims can be summed up by saying that it must answer the question: Who? What is it? Where? Why? And how?
The 5 objectives of project planning
- Time planning: structuring tasks to meet delivery deadlines
- Resource management: defining the human and material resources required for the project and allocating them to the right people
- Project monitoring: the schedule enables the project to be monitored and controlled methodically and strategically
- Communication and collaboration: streamlining collaboration, communication and meetings between stakeholders
- Risk management: identifying potential risks, implementing mitigation plans and anticipating response strategies
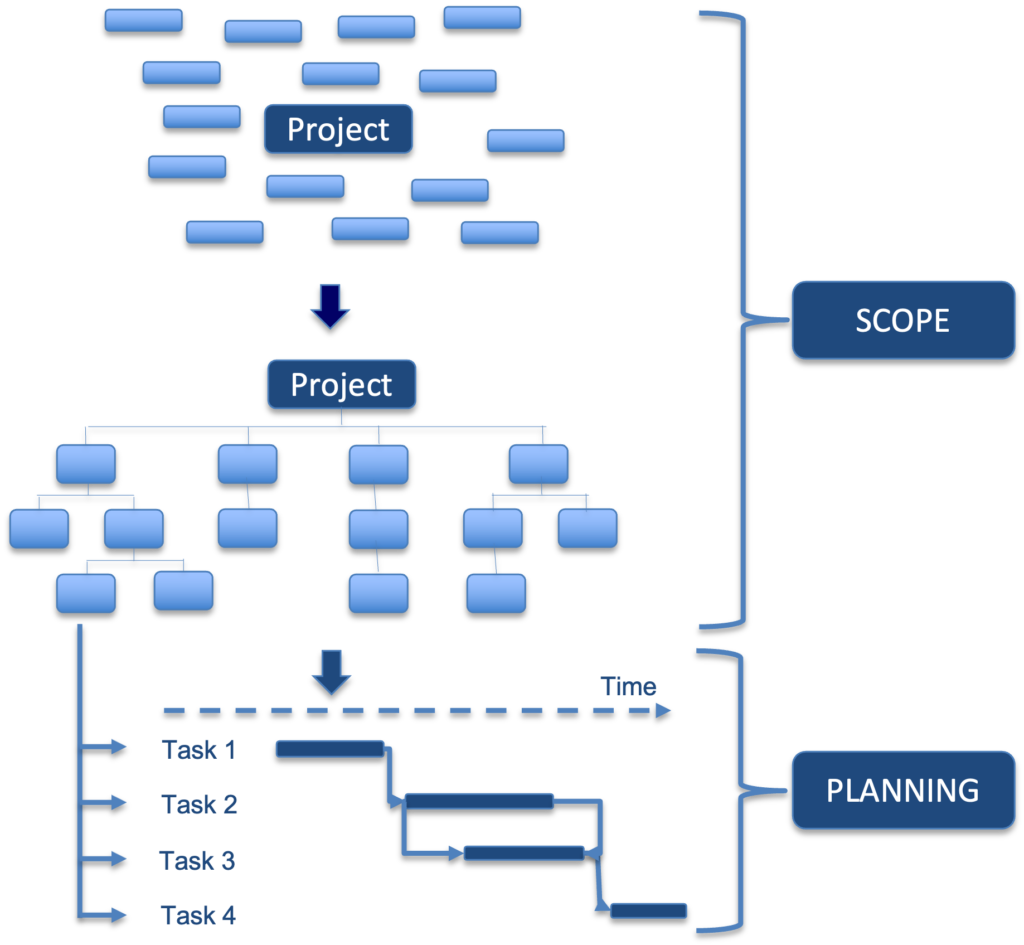
Project planning stages
To be effective and efficient, project planning must be carried out conscientiously, step by step. The essential steps are:
- Project brief: this serves as a roadmap and should be distributed to all stakeholders. It lists essential information such as objectives, resources, timetable, milestones, etc.
- Develop the task organisation chart to break down the scope into accessible and more manageable elements.
- Drafting of the task list: all tasks must be listed in chronological order.
- Definition of task durations: in this stage, a suitable duration must be defined for each of the tasks to be carried out.
- Determining dependencies: it is important to define the relationships between tasks, particularly those that need to be completed before others can be executed.
- Integrate all these elements into your project planning using appropriate software.
The use of project management tools such as Oracle Primavera P6, Oracle Primavera Cloud, Microsoft Projet and Project Online is highly recommended for the successful implementation of the project schedule. PROPRISM can help you create your project schedules and train you in the management software that is essential to their successful design.
The project planning classification levels
There are several levels of project planning classification, which we will describe below. Also, to successfully plan a project, it is advisable to combine these methods.
- Dynamic level: dynamic planning is flexible and can adjust to changes in real time, taking into account the evolution of the project and modifications. This ensures that the plan remains relevant and valid.
- Logical level: logical planning focuses on the coherence and logic of the sequences between project tasks. This ensures that the sequence of activities is coherent and that there are no contradictions in the progress of the project.
- Probabilistic level: this deals with the uncertainties and risks associated with planning. It incorporates probabilistic models to evaluate possible scenarios based on uncertain variables, enabling more realistic estimates of timescales to be made, taking account of contingencies.
- Static level: static scheduling implies a list of tasks with no correlations between them, the schedule is “static” and therefore not modifiable.
The critical path method
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is widely used in project planning. It may seem complex at first, but its usefulness is undeniable. The critical path method consists of organising tasks, their duration and the links between them. These tasks must be carried out one after the other, with no room for manoeuvre. This modelling enables a plan to be created, calculated and then a result to be obtained for analysis. Often, the result will take the form of a Gantt chart, providing a clear view of the tasks, their dependencies and their duration.
The benefits of the critical path method include better time management, better risk management and better analysis of the impact of the project.
In a nutshell
Good project management planning is essential to the success and efficiency of a project. Project planning is based on scheduling, which consists of establishing a sequence of actions to be carried out in order to achieve the objectives set. This involves determining the resources available, the dependencies between tasks, the deadlines to be met and the people responsible for carrying them out.
Project management tools such as Microsoft Project / Project Online, Oracle Primavera P6/OPC/EPPM or agile methods such as Kanban make it easier to create and monitor the schedule. These tools provide a visual representation of the schedule in the form of Gantt charts and other diagrams, which display tasks, their duration, order of execution and progress, thus facilitating the process. Good planning should also take into account all aspects of the project, including task management, resource planning, risk management and the definition of deliverables and deadlines. It must be realistic, taking into account the workload and capacity of the project team. Subsequently, project monitoring is also essential to ensure that the project is progressing in line with the schedule. It is important to set up dashboards and monitoring tools to track the progress of tasks, compliance with deadlines and the achievement of objectives.
A good schedule needs to be flexible. It is important to leave room for manoeuvre to deal with unforeseen events or changes. Agile methods, for example, encourage flexibility and adaptability by dividing the project into sprints or shorter iterations, so that feedback and adjustments can be taken into account as the project progresses.
In short, a good project management plan provides a clear overview of all the stages, tasks, resources and deadlines involved in the project. It must be realistic, flexible, adaptable and constantly monitored and adjusted in line with progress.
Complementary article: Is your project schedule reliable?




